Radon in new buildings
Radon prevention in new construction is important in order to ensure low radon concentrations in indoor air. Radon prevention in the construction phase is easier and less expensive than implementing mitigation measures afterwards. Use of radon-safe building methods is justifiable anywhere in Finland. The aim should be to keep the radon concentration as low as possible, as the higher the radon concentration and the longer you stay in it, the greater the risk of lung cancer associated with radon.
The key question in radon prevention is the blocking or reduction of radon-bearing air flow from the soil. The most common foundation type for low-rise residential buildings in Finland is a floor slab cast inside a footing. Between the slab and the footing, there is normally a gap through which radon can seep into the building. Using lightweight concrete blocks as the foundation wall material can make the situation worse. The same problem is met when lightweight concrete blocks are used as the material of walls in contact with soil in hillside houses or houses with a cellar, instead of cast concrete. These detriments can be easily prevented by sealing the base floor and wall structures and installing radon piping.
A base floor with a crawl space is a radon-safe solution, if radon is prevented from entering the house by sealing base floor joints and penetrations and ensuring sufficient ventilation of the crawl space. Sufficient ventilation is achieved by following the regulations concerning the size and number of vents. The third radon-safe solution is a monolithic slab foundation which has no leaking gaps or joints. The sealing of the penetrations must be ensured also with this solution.
In new buildings, mechanical supply and exhaust ventilation is the best solution for radon prevention. Even if the ventilation is adjusted to balance, the temperature difference between indoor and outdoor air causes underpressure at the floor level. This underpressure forces the radon-bearing air in the soil to flow into the house. However, the building's ventilation must not be adjusted to overpressure due to the risk of moisture damage. Ventilation must always be designed and implemented in accordance with building codes and related instructions.
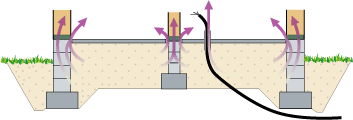
Radon-safe building methods are, as a rule, justifiable in the entire country, as values exceeding the reference level of 200 Bq/m3 without radon prevention is common. It is not worth carrying out soil radon measurements, as radon prevention is cheaper than a radon survey of a single plot of land.
In addition to reducing radon levels, radon-safe building methods can improve indoor air quality in other ways. A radon-safe solution prevents musty odours and any other hazardous gases from soil from seeping into the building. Radon piping also removes moisture from the base floor.
The architect and builder should always be required to comply with the instructions of the RT reference card on radon-safe design and construction. Radon prevention solutions are marked on the foundation, structural and HVAC drawings. During construction, it is important to oversee that radon prevention is carried out as planned.
Methods for radon prevention
The ventilation system of the foundation ensures the control of indoor radon concentration in case there are air leaks remaining in the base floor structures from the construction phase or if they are created later during the life cycle of the building. The purpose of the ventilation system is to ventilate the air in the voids in the sub-surface drainage layer and to create underpressure in the foundation, if necessary. Then the amount of air flowing from the foundation into the house and the radon concentration decrease.
Radon piping is installed under the floor, in the capillary break layer below the base floor thermal insulation. The radon vent duct is taken to the roof already at the construction phase to allow natural ventilation. With this, it is possible to avoid modifications in the finished building, which are required for retrofitting the vent pipe if an extractor fan has to be connected to the radon piping. Typically, passive radon piping reduces the radon concentration by 20 to 60 per cent.
When the building is completed, a control radon measurement is recommended. In order to obtain a reliable result, heating and ventilation systems must be completed and in normal use. If the radon concentration exceeds the reference value of 200 Bq/m3 despite the prevention measures carried out in the construction phase, an extractor fan is installed in the exhaust duct. The RT reference card gives more detailed instructions on the dimensioning of the extractor fan and air flow. Connecting an extractor fan to the radon piping typically reduces the radon concentration by 60 to 95 per cent.
The suction ductwork may be designed as looped or branched. The piping is located at least 200 mm below thermal insulation. The ventilation system can be implemented using the available construction and ventilation equipment. There are also radon piping packages on the market that are suitable for low-rise residential buildings and contain all the pipes, connectors and accessories.
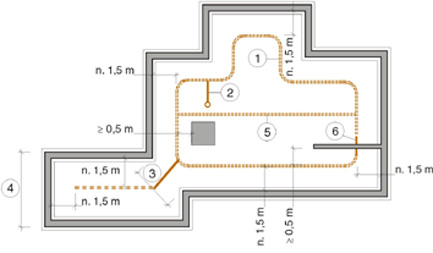
1. Suction ductwork, plastic underdrainage pipe
- distance from the foundation wall approximately 1.5 meters
- minimum distance from building elements that penetrate slab 0.5 m
2. Transfer duct and exhaust duct, plastic underdrainage pipe.
3. If there are points in the suction duct route that are narrower than 3 metres, a tight pipe, e.g. a stormwater drain pipe, should be used in that area.
4. If the frame depth of the building is from three to four metres, a looped suction duct can be replaced with a single longitudinal suction duct with a blocked end.
5. If the frame depth is more than 10 metres, an additional suction duct is needed, placed along the centre line of the building.
6. At the foundation penetration, the suction duct is replaced with a leak-tight pipe.
Branched piping is the best solution for semi-detached houses and row houses. As extremely coarse backfill materials that are highly permeable to air are nowadays used under the slab, the efficiency of looped piping even in a semidetached house may be sufficient only in the part of the house in which the exhaust duct is installed. On the other side of the house, air flow may be insufficient. For more detailed instructions, see the RT reference card.
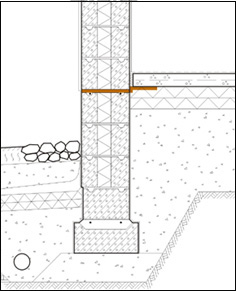
The aim of the seals is to make the floor structures and joints as tight as possible. The connection between the foundation wall/footing and the ground slab is sealed with rubberized bitumen felt as shown in the examples below.
The bitumen felt is installed on top of the foundation wall and under the ground-supported slab at a 150 mm minimum width, with the sand surface and cast surface against each other. The felt is installed so that it will not break or become detached from the structures as a result of shrinkage, subsidence or other movements.
The instructions are applicable to all types of footing details. The recommended material is category TL2 rubberized bitumen felt with a polyester support layer, such as K-MS 170/3000, weldable or glueable. The RT reference card includes figures illustrating radon prevention of load-bearing partitions and ground-supported walls.
The felt prevents radon-containing soil air from flowing inside the building.
Figures of the installation of a rubberized bitumen felt.
Figures of the installation of a rubberized bitumen felt
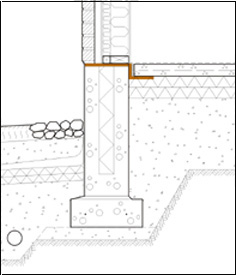
Penetrations can constitute a substantial route for leakage of radon-bearing air from the soil.
Penetrations made for electric cables and radiator, water and drain pipes that are led into the building from below the base floor (and their casing tubes) can be a route for radon leakage into the building. It is also important to seal any hatch structures in the slab. The RT reference card includes examples of the sealing of individual pipes and pipe groups. The sealing is conducted using elastic sealing compound after defining the area to be sealed with a suitable strip or filler.
Penetrations and slab joints must be sealed throughout the building. Neglecting the sealing in the engineering and utility services room or storage room, for example, may lead to a considerable increase in the radon concentration in the house.
According to the Building Act, anyone undertaking a construction project must ensure that the building is designed and constructed in such a way that its indoor air is healthy and safe. The reference value for new buildings in accordance with the Decree of the Ministry of Social Affairs and Health pursuant to the Radiation Act is 200 Bq/m3.
Building codes related to radon have been issued by the Decree of the Ministry of the Environment on Foundation Structures (465/2014) and on Indoor Climate and Ventilation of Buildings (1009/2017). According to the Decree on Foundation Structures (section 4), the radon risks of the construction site must be taken into account in the design and implementation. According to the Decree on Indoor Climate and Ventilation of Buildings (section 5), no physical agents, such as radon, may be present in the indoor air in quantities harmful to health. The ventilation designer must plan the exterior and exhaust air flows of the building in such a way that the structures do not suffer from long-term moisture stress that damages the structures due to overpressure or the transfer of radon from the soil to indoor air due to underpressure (section 21).
Municipal building codes may contain more specific requirements for radon-safe construction.
Finally, remember to carry out radon measurements for at least two months
After the completion of the building, it is advisable to carry out a radon concentration measurement to ensure that radon protection is successful and to detect possible construction errors. The measurement should be carried out immediately during the first year when the warranty is still valid and the construction company is obligated to take any necessary measures to reduce the radon concentration. In order to obtain a reliable result, heating and ventilation systems must be completed and in normal use. If the radon concentration exceeds the reference value of 200 Bq/m3, it is easy to reduce the radon concentration by connecting an extractor fan to the exhaust duct.
Do you have questions about radon prevention?
You should first contact the building supervision of your municipality or the supervisor or structural designer responsible for your construction project.
[email protected]